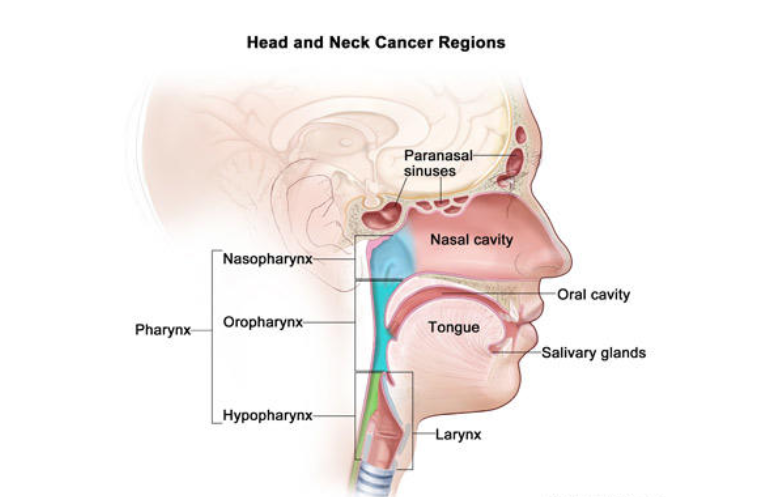
Head Neck Cancer
Cancer is a disease that occurs when abnormal cells in the body grow uncontrollably, leading to tumors or affecting the blood and immune system. There are various types of cancers, each affecting different organs and requiring specific treatment approaches. Early detection and timely medical intervention play a crucial role in improving survival rates.
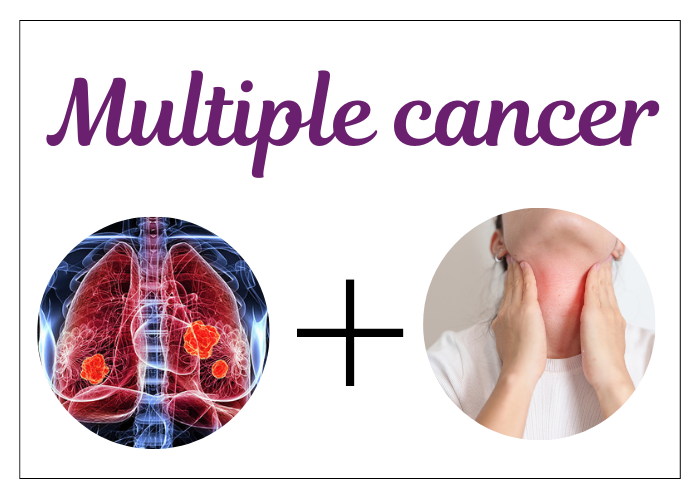
Multiple cancer refers to cases where an individual develops more than one type of cancer simultaneously or at different times. This can be either:
- Synchronous cancer – Two or more primary cancers diagnosed at the same time.
- Metachronous cancer – A second primary cancer occurring after treatment for the first cancer.
People who have had cancer once are at a higher risk of developing another, especially if genetic factors or environmental exposures play a role.
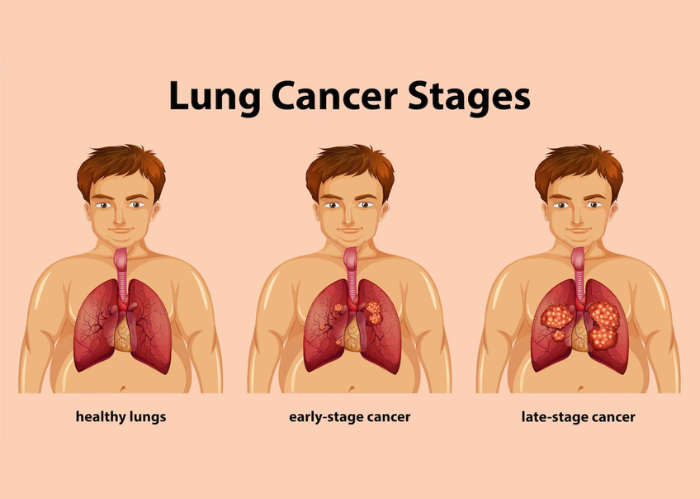
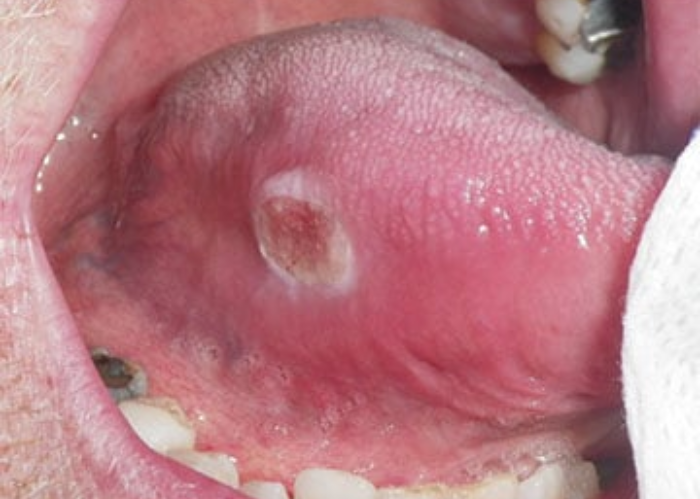
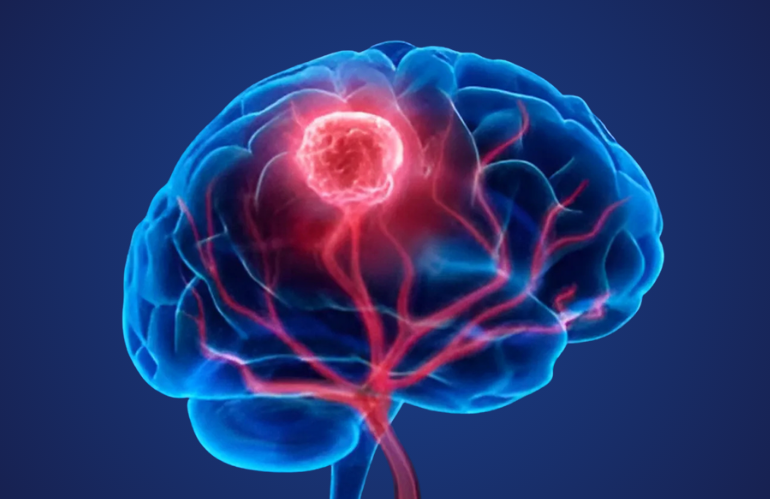
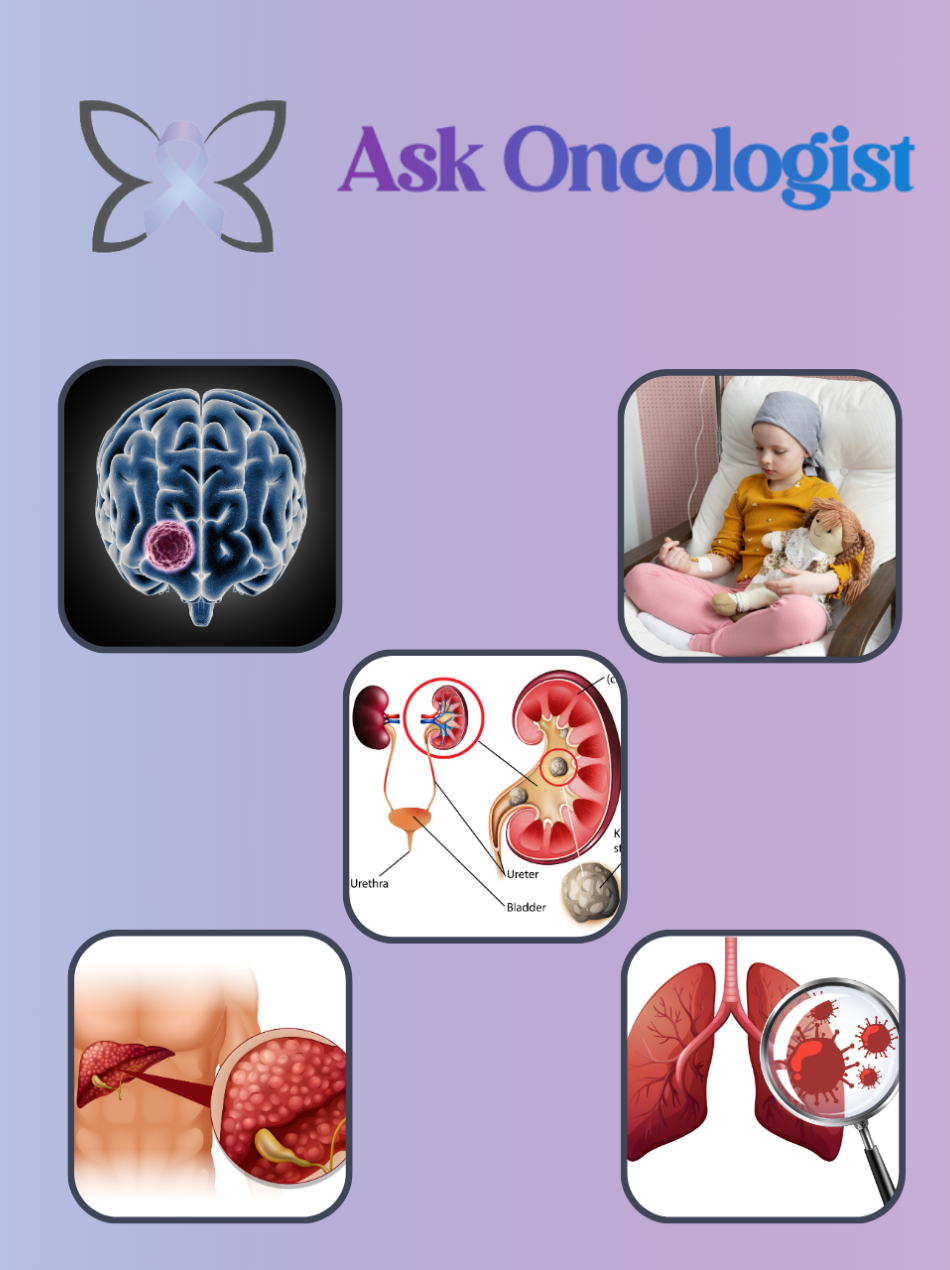
Individuals with head and neck cancer are at an increased risk of developing lung cancer, particularly due to tobacco and alcohol use.
- Symptoms: Persistent cough, hoarseness, throat pain, difficulty swallowing.
- Causes: Smoking, heavy alcohol consumption, human papillomavirus (HPV).
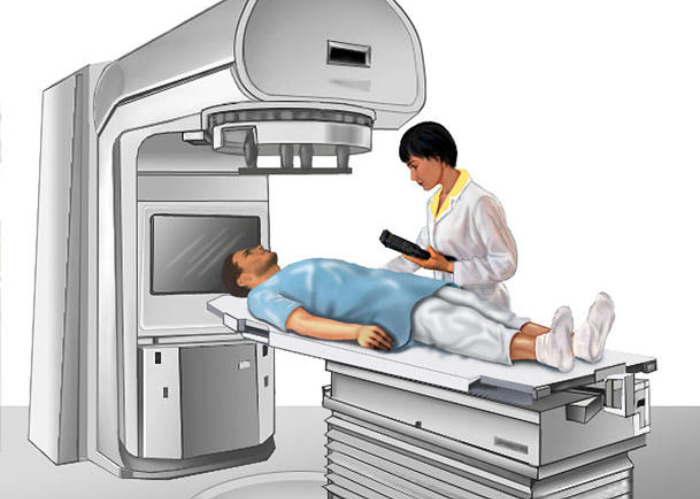
- Treatment: Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy.
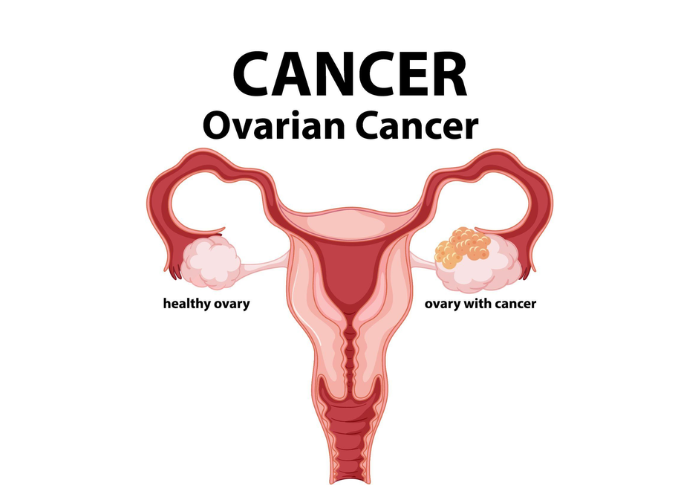
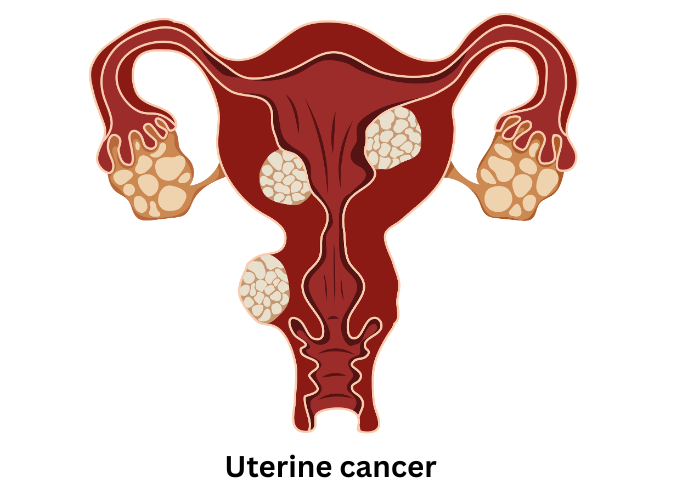
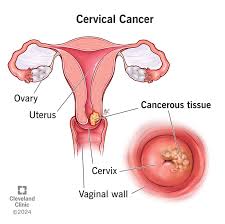
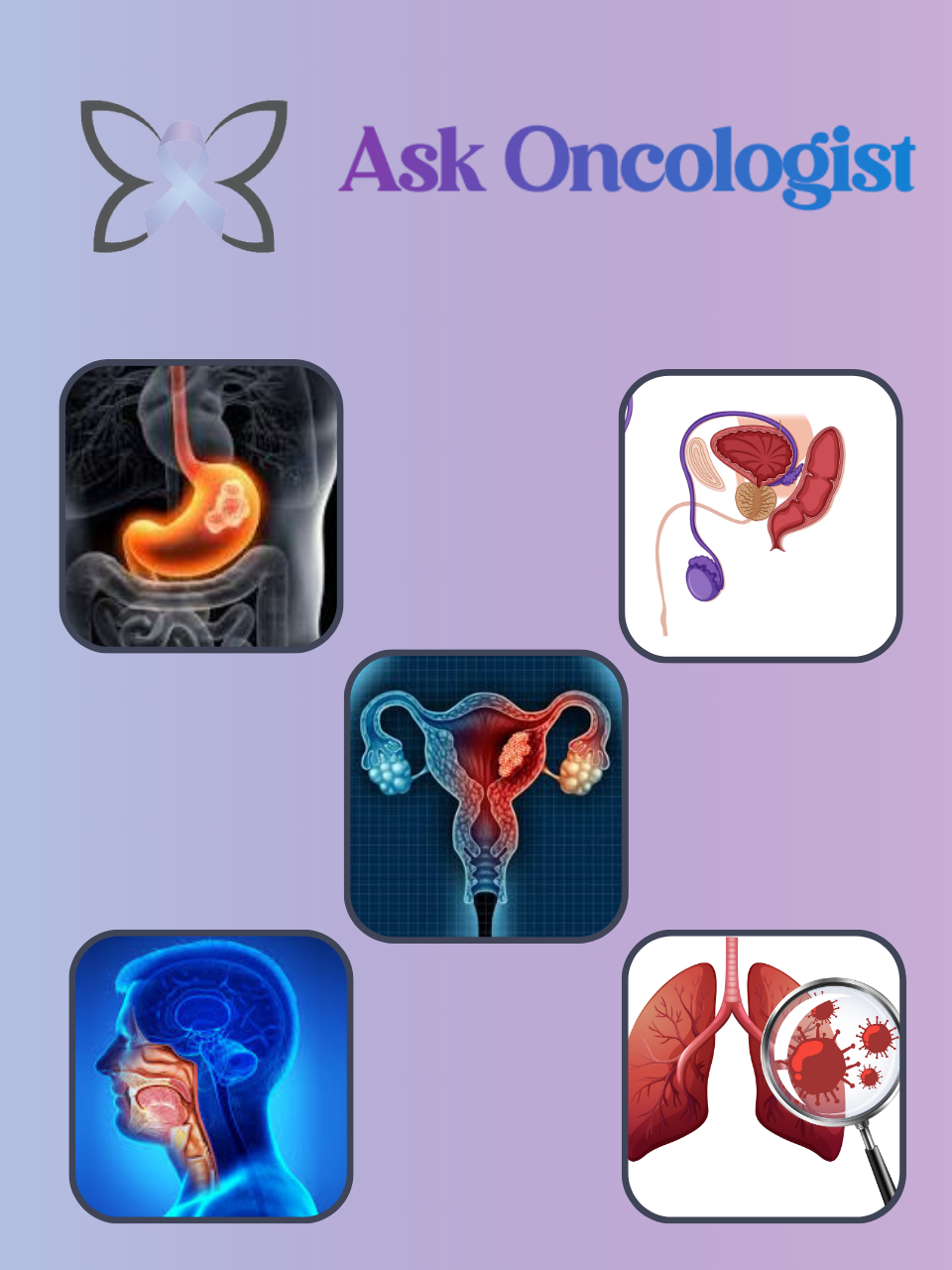
Women with a BRCA1 or BRCA2 genetic mutation are more likely to develop both breast and ovarian cancer.
- Symptoms: Breast lumps, nipple discharge, bloating, pelvic pain.
- Causes: Genetic mutations, hormone imbalances, obesity.
- Treatment: Lumpectomy, mastectomy, hormone therapy, targeted therapy.
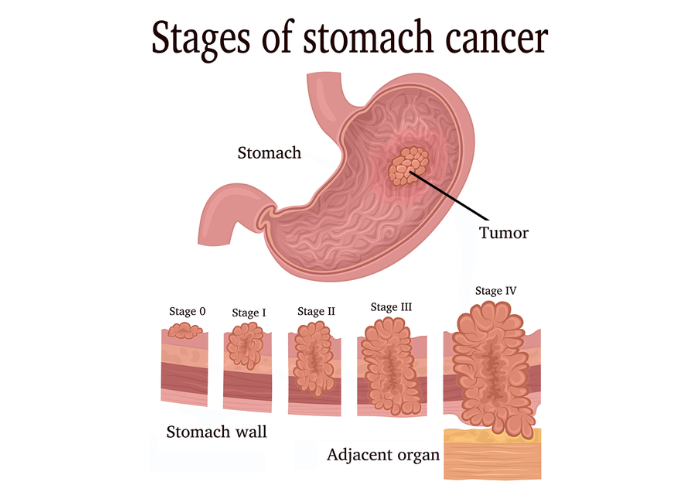
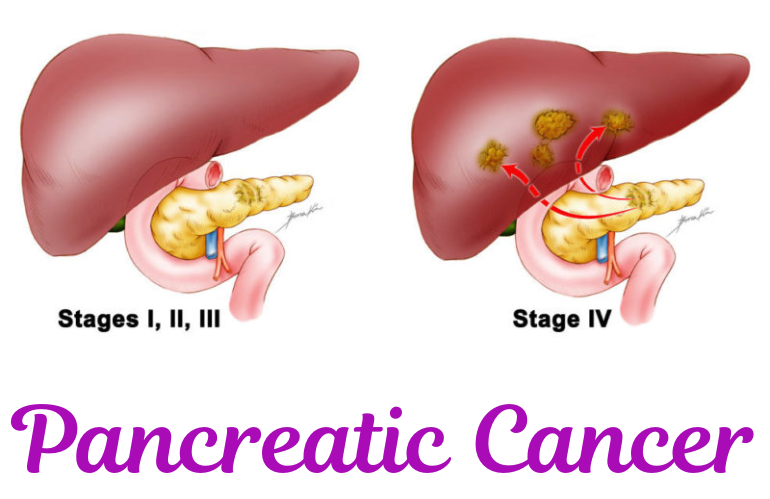
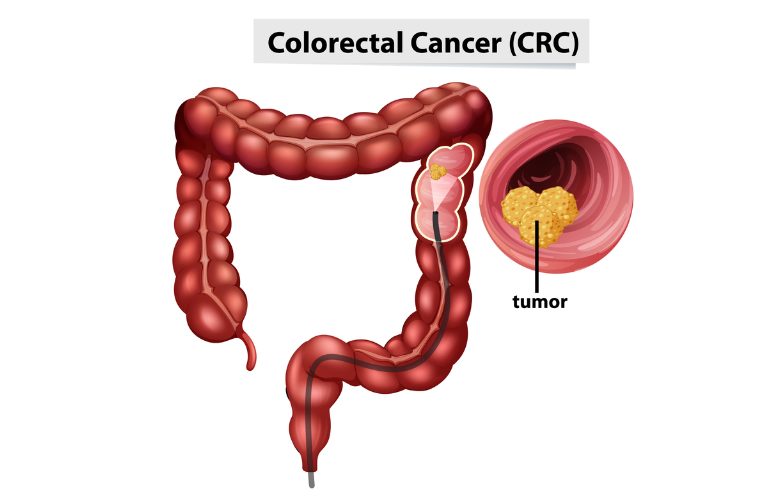
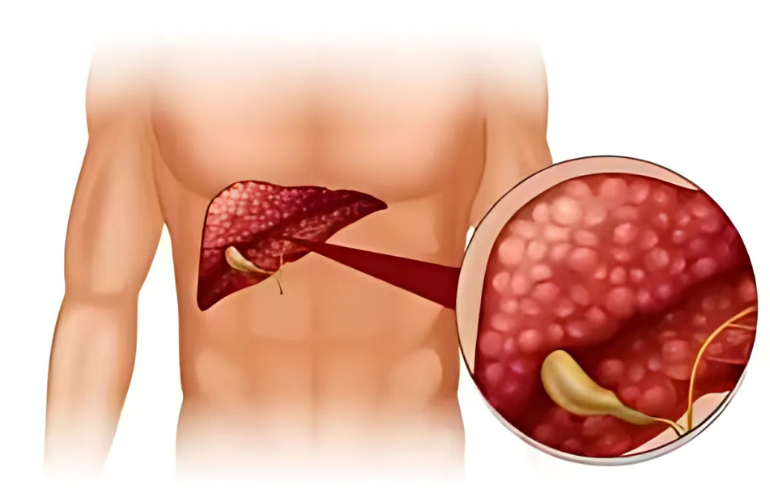
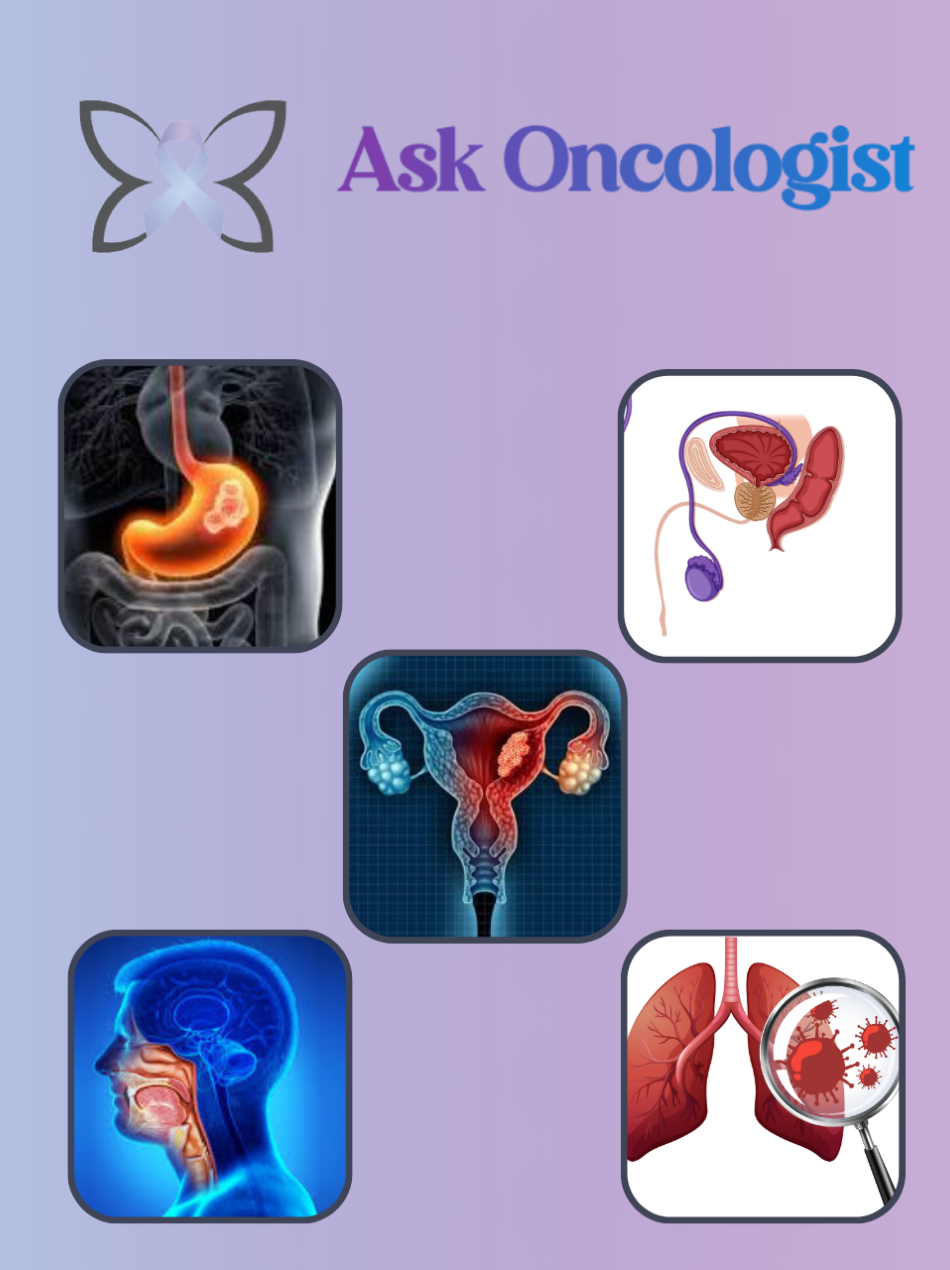
Individuals with a family history of gastrointestinal cancers have a higher chance of developing both colorectal and stomach cancer.
- Symptoms: Abdominal pain, blood in stool, indigestion, unexplained weight loss.
- Causes: Diet high in processed foods, smoking, Helicobacter pylori infection.
- Treatment: Surgery, radiation therapy, targeted drugs, lifestyle modifications.
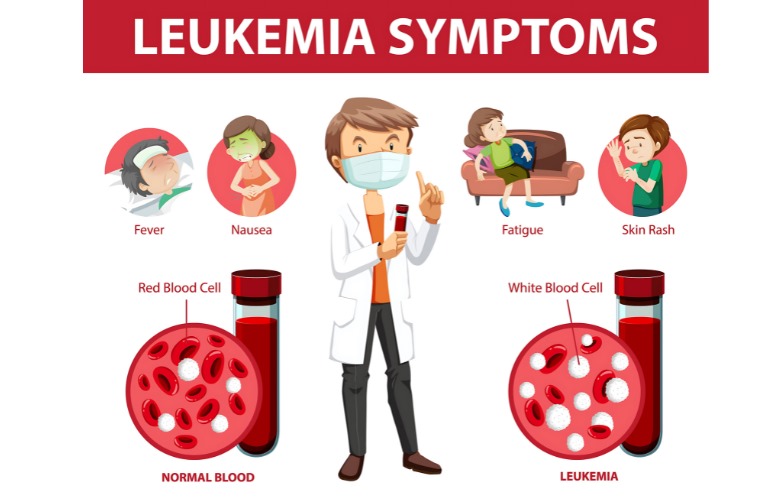
Prolonged exposure to harmful chemicals or radiation can increase the risk of developing both leukemia (blood cancer) and skin cancer.
- Symptoms: Frequent infections, pale skin, easy bruising, skin sores that do not heal.
- Causes: Sun exposure, immune system disorders, previous cancer treatments.
- Treatment: Chemotherapy, stem cell transplant, targeted therapy.
Early diagnosis is key to better outcomes. A combination of the following tests helps detect multiple cancers:
Biopsy – Identifies cancerous tissue.
Blood Tests – Detects abnormal cell activity.
Imaging Tests – CT scan, MRI, PET scan for cancer spread.
Genetic Testing – Determines inherited cancer risk.
If you are at risk, regular cancer screenings can aid in early detection and treatment.
Patients diagnosed with multiple cancers may require a combination of treatment strategies based on their overall health condition.
Radiation Therapy – Targets cancer cells with minimal damage to surrounding tissues.
Chemotherapy – Destroys cancer cells and prevents further spread.
Surgery – Removes tumors when feasible.
Immunotherapy – Boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer.
Targeted Therapy – Focuses on specific cancer mutations for effective treatment.
At AskOncologist.com, we provide personalized treatment plans to manage multiple cancers effectively.
While some factors are unavoidable, certain lifestyle changes can lower cancer risks:
Quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption
Maintain a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
Exercise regularly to boost immunity and maintain a healthy weight
Get regular cancer screenings if you have a family history
Practice sun safety to reduce the risk of skin cancer
Taking preventive measures and seeking expert medical advice can significantly improve long-term health outcomes.
ConclusionMultiple cancers pose unique challenges, but with early detection, proper treatment, and lifestyle modifications, patients can achieve better health outcomes. If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms, seeking prompt medical attention is crucial.
For expert consultation on multiple cancers, visit AskOncologist.com today.
Schedule an appointment with Dr. K. Pradeep Bhaskar, leading oncologist in Kakinada.
Head Neck Cancer
Cancer is a disease that occurs when abnormal cells in the body grow uncontrollably, leading to tumors or affecting the blood and immune system. There are various types of cancers, each affecting different organs and requiring specific treatment approaches. Early detection and timely medical intervention play a crucial role in improving survival rates.

Multiple cancer refers to cases where an individual develops more than one type of cancer simultaneously or at different times. This can be either:
- Synchronous cancer – Two or more primary cancers diagnosed at the same time.
- Metachronous cancer – A second primary cancer occurring after treatment for the first cancer.
People who have had cancer once are at a higher risk of developing another, especially if genetic factors or environmental exposures play a role.
Individuals with head and neck cancer are at an increased risk of developing lung cancer, particularly due to tobacco and alcohol use.
- Symptoms: Persistent cough, hoarseness, throat pain, difficulty swallowing.
- Causes: Smoking, heavy alcohol consumption, human papillomavirus (HPV).
- Treatment: Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy.
Women with a BRCA1 or BRCA2 genetic mutation are more likely to develop both breast and ovarian cancer.
- Symptoms: Breast lumps, nipple discharge, bloating, pelvic pain.
- Causes: Genetic mutations, hormone imbalances, obesity.
- Treatment: Lumpectomy, mastectomy, hormone therapy, targeted therapy.
Individuals with a family history of gastrointestinal cancers have a higher chance of developing both colorectal and stomach cancer.
- Symptoms: Abdominal pain, blood in stool, indigestion, unexplained weight loss.
- Causes: Diet high in processed foods, smoking, Helicobacter pylori infection.
- Treatment: Surgery, radiation therapy, targeted drugs, lifestyle modifications.
Prolonged exposure to harmful chemicals or radiation can increase the risk of developing both leukemia (blood cancer) and skin cancer.
- Symptoms: Frequent infections, pale skin, easy bruising, skin sores that do not heal.
- Causes: Sun exposure, immune system disorders, previous cancer treatments.
- Treatment: Chemotherapy, stem cell transplant, targeted therapy.
Early diagnosis is key to better outcomes. A combination of the following tests helps detect multiple cancers:
Biopsy – Identifies cancerous tissue.
Blood Tests – Detects abnormal cell activity.
Imaging Tests – CT scan, MRI, PET scan for cancer spread.
Genetic Testing – Determines inherited cancer risk.
If you are at risk, regular cancer screenings can aid in early detection and treatment.
Patients diagnosed with multiple cancers may require a combination of treatment strategies based on their overall health condition.
Radiation Therapy – Targets cancer cells with minimal damage to surrounding tissues.
Chemotherapy – Destroys cancer cells and prevents further spread.
Surgery – Removes tumors when feasible.
Immunotherapy – Boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer.
Targeted Therapy – Focuses on specific cancer mutations for effective treatment.
At AskOncologist.com, we provide personalized treatment plans to manage multiple cancers effectively.
While some factors are unavoidable, certain lifestyle changes can lower cancer risks:
Quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption
Maintain a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
Exercise regularly to boost immunity and maintain a healthy weight
Get regular cancer screenings if you have a family history
Practice sun safety to reduce the risk of skin cancer
Taking preventive measures and seeking expert medical advice can significantly improve long-term health outcomes.
ConclusionMultiple cancers pose unique challenges, but with early detection, proper treatment, and lifestyle modifications, patients can achieve better health outcomes. If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms, seeking prompt medical attention is crucial.
For expert consultation on multiple cancers, visit AskOncologist.com today.
Schedule an appointment with Dr. K. Pradeep Bhaskar, leading oncologist in Kakinada.
📝 Latest Comments
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!
Head Neck Cancer
Cancer is a disease that occurs when abnormal cells in the body grow uncontrollably, leading to tumors or affecting the blood and immune system. There are various types of cancers, each affecting different organs and requiring specific treatment approaches. Early detection and timely medical intervention play a crucial role in improving survival rates.

Multiple cancer refers to cases where an individual develops more than one type of cancer simultaneously or at different times. This can be either:
- Synchronous cancer – Two or more primary cancers diagnosed at the same time.
- Metachronous cancer – A second primary cancer occurring after treatment for the first cancer.
People who have had cancer once are at a higher risk of developing another, especially if genetic factors or environmental exposures play a role.
Individuals with head and neck cancer are at an increased risk of developing lung cancer, particularly due to tobacco and alcohol use.
- Symptoms: Persistent cough, hoarseness, throat pain, difficulty swallowing.
- Causes: Smoking, heavy alcohol consumption, human papillomavirus (HPV).
- Treatment: Surgery, radiation therapy, chemotherapy, immunotherapy.
Women with a BRCA1 or BRCA2 genetic mutation are more likely to develop both breast and ovarian cancer.
- Symptoms: Breast lumps, nipple discharge, bloating, pelvic pain.
- Causes: Genetic mutations, hormone imbalances, obesity.
- Treatment: Lumpectomy, mastectomy, hormone therapy, targeted therapy.
Individuals with a family history of gastrointestinal cancers have a higher chance of developing both colorectal and stomach cancer.
- Symptoms: Abdominal pain, blood in stool, indigestion, unexplained weight loss.
- Causes: Diet high in processed foods, smoking, Helicobacter pylori infection.
- Treatment: Surgery, radiation therapy, targeted drugs, lifestyle modifications.
Prolonged exposure to harmful chemicals or radiation can increase the risk of developing both leukemia (blood cancer) and skin cancer.
- Symptoms: Frequent infections, pale skin, easy bruising, skin sores that do not heal.
- Causes: Sun exposure, immune system disorders, previous cancer treatments.
- Treatment: Chemotherapy, stem cell transplant, targeted therapy.
Early diagnosis is key to better outcomes. A combination of the following tests helps detect multiple cancers:
Biopsy – Identifies cancerous tissue.
Blood Tests – Detects abnormal cell activity.
Imaging Tests – CT scan, MRI, PET scan for cancer spread.
Genetic Testing – Determines inherited cancer risk.
If you are at risk, regular cancer screenings can aid in early detection and treatment.
Patients diagnosed with multiple cancers may require a combination of treatment strategies based on their overall health condition.
Radiation Therapy – Targets cancer cells with minimal damage to surrounding tissues.
Chemotherapy – Destroys cancer cells and prevents further spread.
Surgery – Removes tumors when feasible.
Immunotherapy – Boosts the body’s immune system to fight cancer.
Targeted Therapy – Focuses on specific cancer mutations for effective treatment.
At AskOncologist.com, we provide personalized treatment plans to manage multiple cancers effectively.
While some factors are unavoidable, certain lifestyle changes can lower cancer risks:
Quit smoking and limit alcohol consumption
Maintain a healthy diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
Exercise regularly to boost immunity and maintain a healthy weight
Get regular cancer screenings if you have a family history
Practice sun safety to reduce the risk of skin cancer
Taking preventive measures and seeking expert medical advice can significantly improve long-term health outcomes.
ConclusionMultiple cancers pose unique challenges, but with early detection, proper treatment, and lifestyle modifications, patients can achieve better health outcomes. If you or a loved one is experiencing symptoms, seeking prompt medical attention is crucial.
For expert consultation on multiple cancers, visit AskOncologist.com today.
Schedule an appointment with Dr. K. Pradeep Bhaskar, leading oncologist in Kakinada.
📝 Latest Comments
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!














📝 Latest Comments
No comments yet. Be the first to comment!